Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly become one of the most transformative technologies of our time. From healthcare and education to finance and public services, AI systems are now shaping decisions that impact millions of lives every single day. But as AI becomes more powerful in 2025, it also raises serious questions about ethics, fairness, and bias. These concerns are no longer limited to research papers—they directly affect how businesses, governments, and individuals use technology.

Why AI Ethics and Fairness Matter in 2025
In 2025, AI ethics and fairness are more critical than ever because AI is no longer a future trend—it’s a present reality. Companies rely on machine learning algorithms for recruitment, banks use AI for credit scoring, and hospitals depend on AI for diagnosis. If these systems are not designed with fairness and ethical principles, they risk reinforcing discrimination and creating bias in decision-making.
A fair and ethical AI ensures transparency, accountability, and trust. Without these, users may lose confidence in technology, governments may impose stricter regulations, and organizations may face reputational and financial damage. This makes AI fairness not just a moral responsibility, but also a business necessity in 2025.
Growing Concerns Around AI Bias
AI bias occurs when algorithms unintentionally favor certain groups over others due to flawed data, poor design, or hidden assumptions in the system. In recent years, we’ve seen real-world examples:
- Hiring tools that favored male candidates over female ones.
- Healthcare AI systems that gave less accurate results for minority patients.
- Predictive policing algorithms that unfairly targeted specific communities.
As we step into 2025, these challenges have become even more visible. Bias in AI systems is now recognized as one of the biggest threats to responsible AI development. Governments, businesses, and global organizations are all working on solutions, but the journey to a bias-free AI future is still ongoing.
Understanding AI Ethics
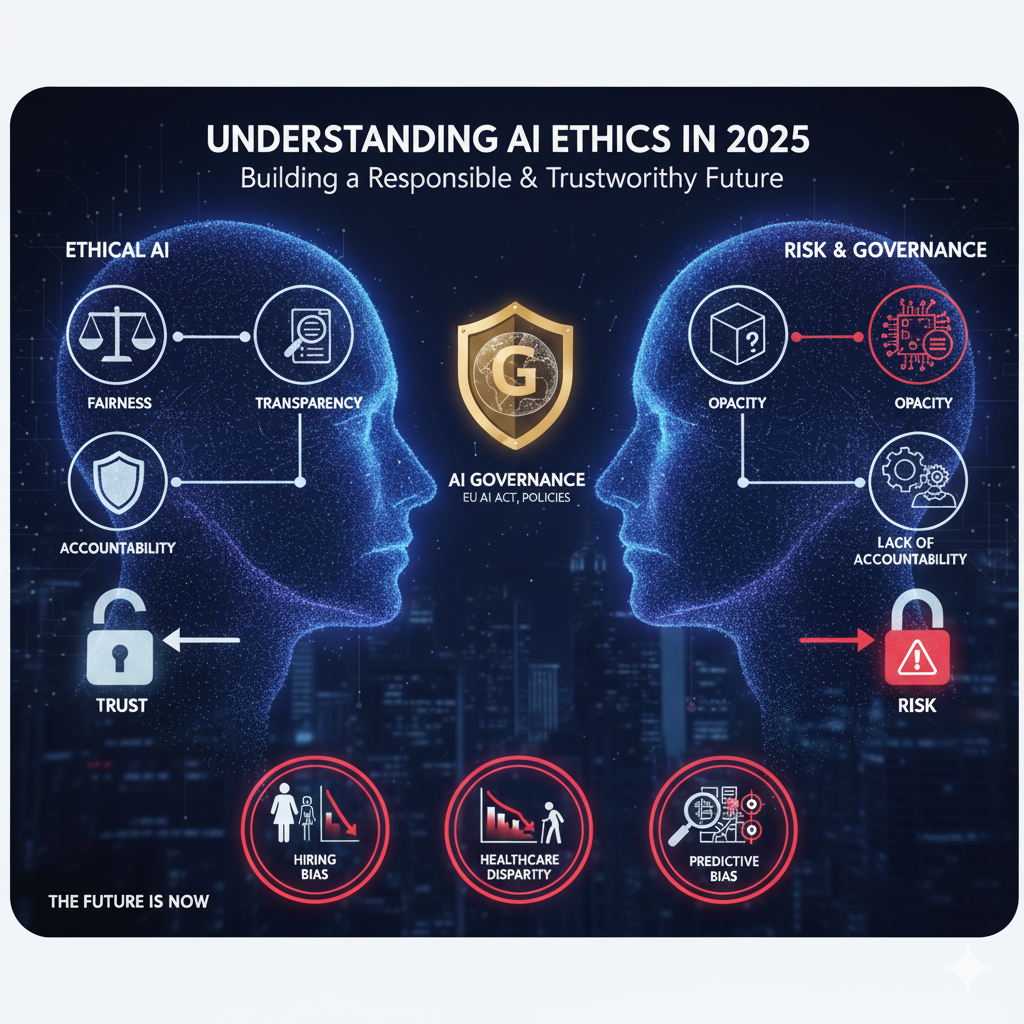
Artificial Intelligence is powerful, but without the right ethical framework, it can cause more harm than good. This is why AI ethics has become one of the most important discussions in technology today. It focuses on making sure that AI is designed, deployed, and used in a way that benefits society, respects human rights, and avoids harmful consequences.
What is AI Ethics?
AI ethics refers to the set of moral principles and guidelines that govern how artificial intelligence should be created and used. It addresses critical questions such as:
- Is the AI system fair and unbiased?
- Can its decisions be explained and understood?
- Does it respect privacy, equality, and human dignity?
In simple terms, AI ethics is about ensuring that technology serves human values rather than replacing or harming them. Without ethical guidelines, AI systems may unintentionally reinforce inequality or make decisions that are harmful to certain groups.
Core Principles of AI Ethics (Transparency, Fairness, Accountability)
The foundation of ethical AI lies in three major principles:
- Transparency – AI systems should not work as “black boxes.” Users and regulators must be able to understand how decisions are made, especially in sensitive areas like healthcare or criminal justice.
- Fairness – AI must provide equal treatment to all individuals, regardless of gender, race, age, or background. This includes detecting and removing bias from data and algorithms.
- Accountability – Developers, businesses, and governments must take responsibility for AI outcomes. If an AI system makes a harmful decision, there should be clear accountability, not just excuses of “the algorithm did it.”
These principles are becoming global standards for responsible AI development in 2025.
Role of AI Governance in 2025
As AI spreads into every industry, the role of AI governance has become critical. AI governance refers to the policies, frameworks, and laws designed to regulate how AI is built and used.
In 2025, many governments and organizations are introducing stricter rules to ensure AI systems are ethical and fair. For example:
- The EU AI Act sets strong regulations on high-risk AI systems.
- Countries like the US, UK, and China are working on ethical AI policies.
- Companies are forming AI ethics boards to monitor transparency and accountability.
The goal of AI governance is simple: to make AI systems trustworthy, bias-free, and human-centered. Without governance, AI risks becoming a tool of exploitation instead of progress.
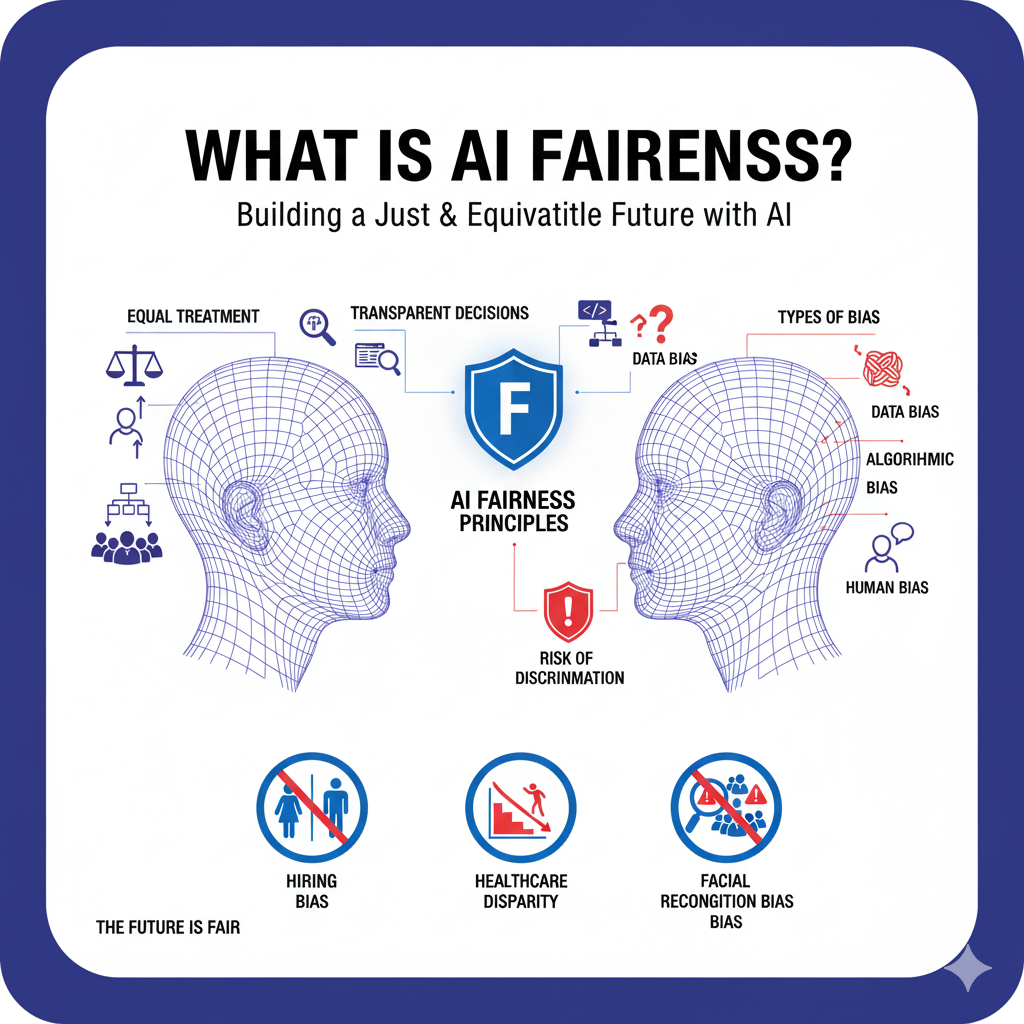
What is AI Fairness?
AI Fairness simply means that artificial intelligence systems should treat all people fairly, equally, and without discrimination. In other words, when AI makes decisions—whether it’s approving a loan, screening job candidates, or recommending medical treatment—it must do so without favoring one group over another.
Unfortunately, AI often reflects the biases of the data it is trained on. For example, if an algorithm is trained mostly on data from one demographic, it may unintentionally make unfair predictions about other groups. That’s why AI fairness has become one of the most important areas of discussion in 2025.
Fairness in AI is not just about “removing bias”—it’s about building trust, accountability, and equality into the design of intelligent systems.
Defining Fairness in Artificial Intelligence
Fairness in AI refers to the absence of unjust bias, favoritism, or discrimination in algorithmic decision-making. An AI system is considered fair if:
- It gives equal opportunities to all users.
- It does not disadvantage people based on gender, race, age, religion, or social background.
- Its decision-making process can be explained and justified.
In simple terms, AI fairness = equal treatment + transparent decisions.
Types of Bias in AI Systems
Bias in AI can appear in many different forms, including:
- Data Bias – When the training dataset itself is unbalanced or incomplete. Example: A medical AI trained only on data from one region may not work well for global populations.
- Algorithmic Bias – When the model design favors certain outcomes due to flawed assumptions.
- Human Bias – Developers’ own unconscious beliefs may influence how AI systems are built.
- Societal Bias – When AI reflects existing inequalities in society (e.g., wage gap, underrepresentation in leadership).
Understanding these biases is the first step toward achieving fairness in AI.
Real-World Examples of AI Fairness Issues
- Hiring Tools – Some AI recruitment systems gave preference to male candidates because training data was historically male-dominated.
- Facial Recognition – Studies found that facial recognition systems had higher error rates for women and people of color.
- Healthcare AI – Algorithms often misdiagnosed minority patients due to lack of diverse medical data.
These examples show that AI fairness is not a theory—it’s a real-world challenge. Organizations that fail to address it risk losing public trust and facing legal consequences.
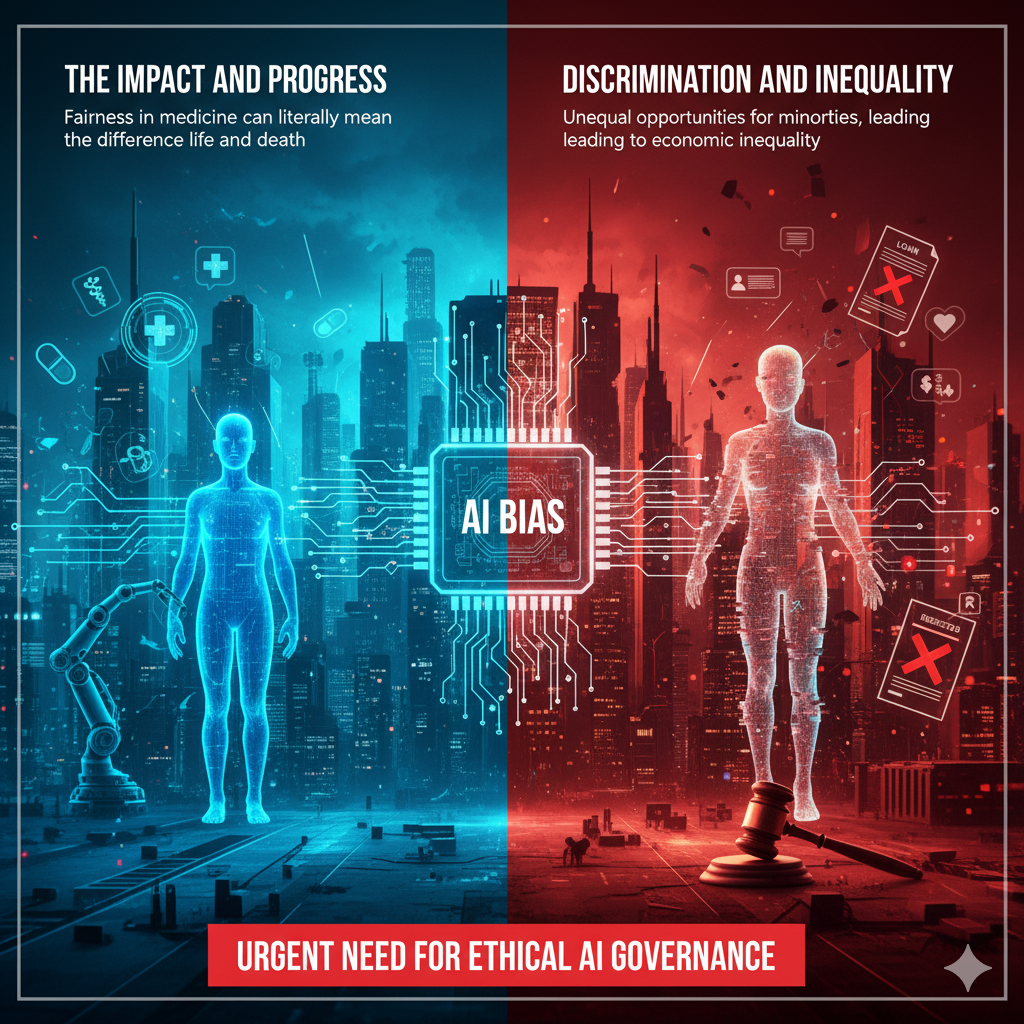
The Impact of AI Bias in 2025
AI has the power to transform lives, but when it is biased, the consequences can be serious, widespread, and unfair. In 2025, the world is experiencing the double-edged nature of AI—on one side, it brings innovation and progress; on the other, it risks reinforcing discrimination and inequality if not handled responsibly.
Bias in AI is not just a technical flaw—it’s a social and ethical issue that affects real people. From job opportunities to medical care, biased algorithms can shape life-changing outcomes.
AI Bias in Healthcare
Healthcare is one of the most sensitive areas where AI bias can cause harm. For example:
- Diagnostic algorithms sometimes perform worse for women and minority patients because they were trained mostly on data from white male populations.
- AI tools predicting disease risk may ignore socio-economic factors, leading to unfair treatment recommendations.
In 2025, addressing bias in healthcare AI is a top priority because fairness in medicine can literally mean the difference between life and death.
AI Bias in Finance and Hiring
Financial institutions and employers increasingly rely on AI for loan approvals, credit scoring, and recruitment. However, biased data can result in:
- Loan applications from certain communities being unfairly rejected.
- Hiring systems preferring male candidates due to historical data imbalance.
- Unequal opportunities for minorities, leading to economic inequality.
This makes AI fairness in finance and employment essential for ensuring equal access to opportunities.
AI Bias in Law Enforcement and Justice Systems
One of the most controversial areas of AI bias is in predictive policing and criminal justice. In some cases:
- AI-based surveillance misidentified people of color more frequently.
- Predictive policing algorithms targeted certain neighborhoods, increasing discrimination.
- Courtroom decision-making systems suggested harsher sentencing for minorities.
Such issues highlight the urgent need for ethical AI governance in law enforcement. Injustice amplified by AI could damage public trust in both technology and the legal system.
Bias Mitigation Strategies for AI
While AI bias is a serious challenge, it is not impossible to fix. In 2025, businesses, researchers, and policymakers are actively working on strategies to create fair, ethical, and bias-free AI systems. The goal is not only to make AI accurate but also to make it trustworthy, transparent, and inclusive.
Here are some of the most effective bias mitigation techniques being used in AI development today:
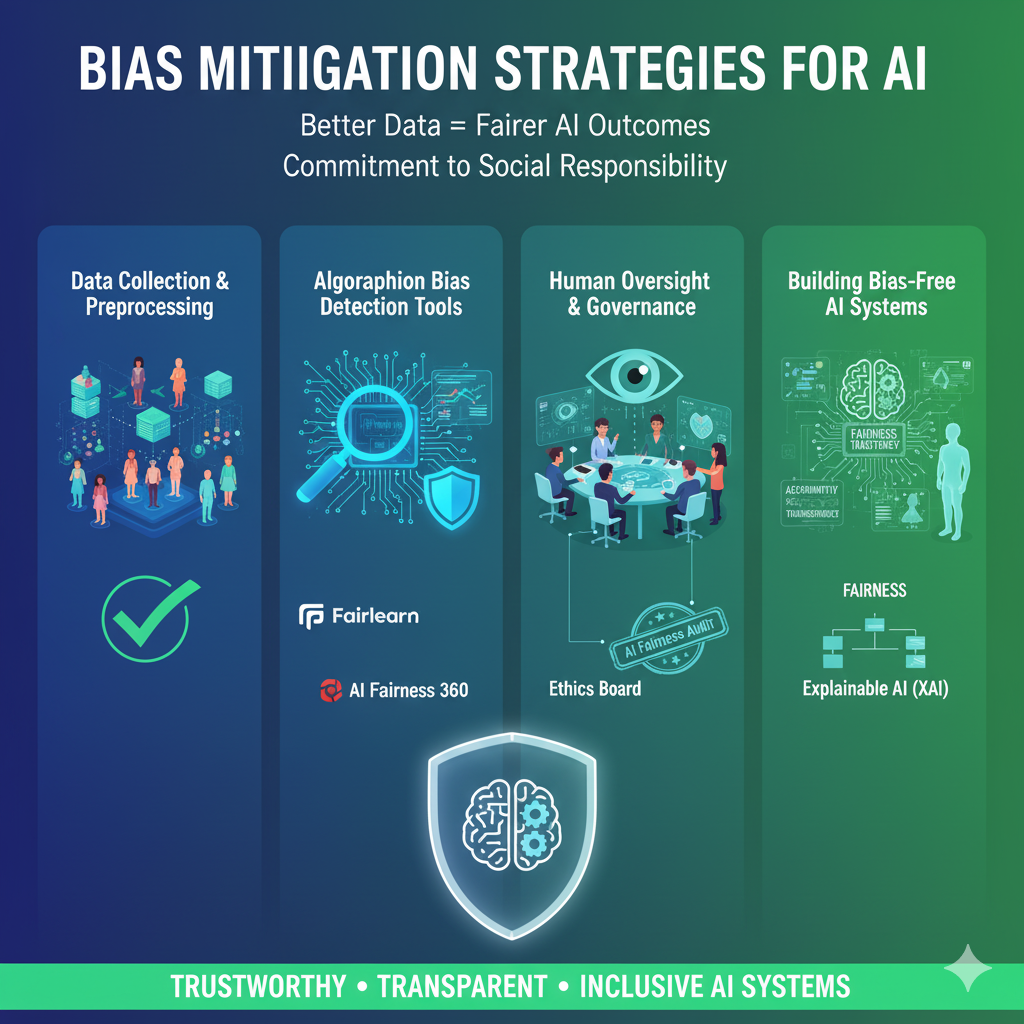
Data Collection and Preprocessing Techniques
Most AI bias originates from biased training data. To fix this:
- Balanced datasets must be collected that represent diverse genders, races, age groups, and communities.
- Preprocessing methods such as data augmentation and sampling can help reduce bias before training.
- Detecting and removing outliers or skewed data points ensures fairer results.
In simple words: Better data = fairer AI outcomes.
Algorithmic Bias Detection Tools
In 2025, several advanced tools and frameworks exist to test AI systems for fairness. For example:
- Fairlearn (Microsoft) and AI Fairness 360 (IBM) help detect and correct bias in machine learning models.
- These tools measure how algorithms treat different demographic groups and provide adjustments for fairness.
- Continuous AI audits are becoming a standard practice for ethical AI development.
Using these bias detection tools ensures that unfair patterns are identified before AI reaches the real world.
Human Oversight and Governance Models
AI should never operate completely without human control. Human oversight is essential because:
- Humans can review AI decisions and identify unfair outcomes.
- Ethics boards and AI governance frameworks can enforce transparency.
- Governments are pushing for mandatory AI fairness audits in high-risk industries like healthcare and finance.
In 2025, combining human judgment with AI efficiency is one of the most reliable strategies for reducing bias.
Building Bias-Free AI Systems for 2025
To achieve long-term fairness, AI developers must:
- Integrate ethical principles (fairness, accountability, transparency) into system design.
- Use explainable AI (XAI) so that decisions are not “black boxes.”
- Regularly update algorithms with new, diverse, and unbiased data.
A bias-free AI system is not just a technical achievement—it’s a commitment to social responsibility and ethical progress.
AI Ethics and Fairness in Different Industries
AI is no longer limited to research labs—it is now deeply integrated into industries that affect our daily lives. From healthcare and education to finance and government, AI decisions directly impact people. This makes ethics and fairness in AI essential for building trust and avoiding discrimination.
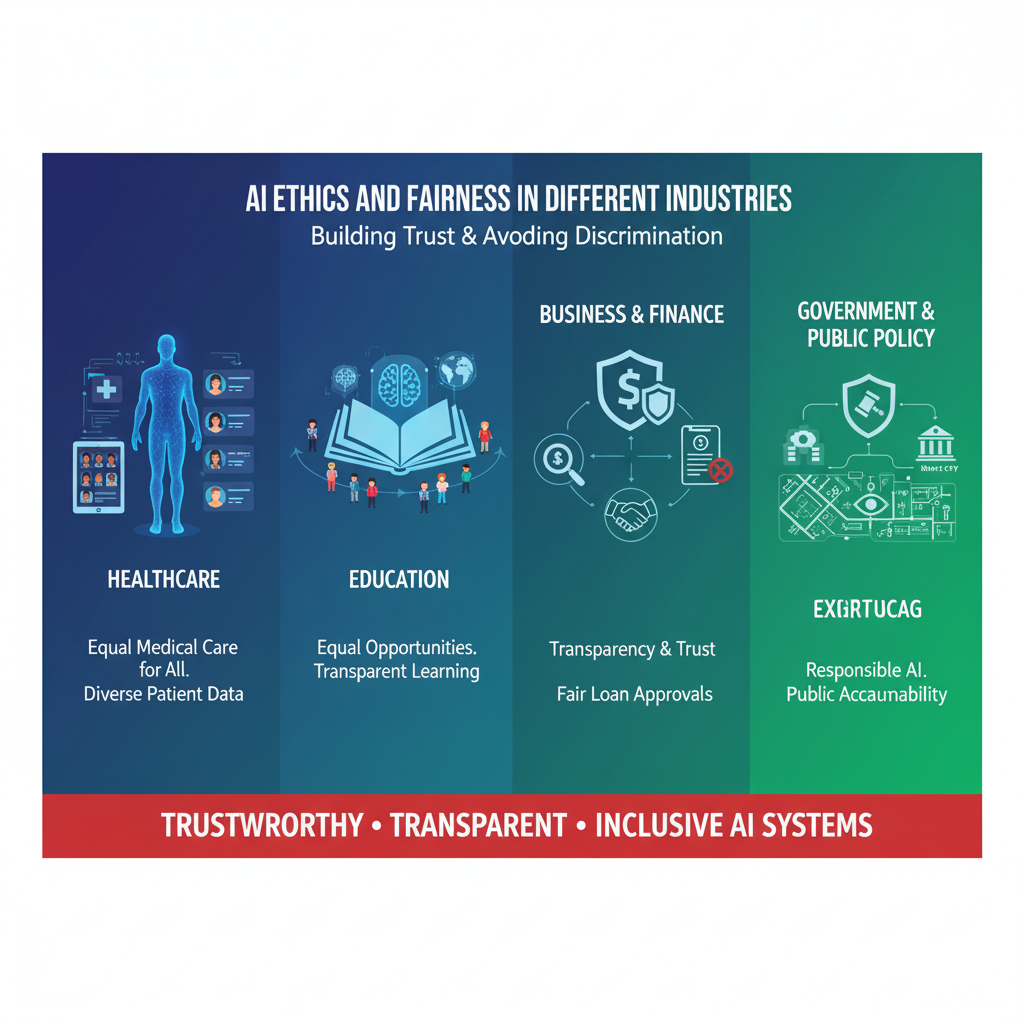
AI in Healthcare: Ensuring Fair Treatment
In healthcare, AI systems are used for diagnosis, patient monitoring, and treatment recommendations. However, if these systems are trained on limited datasets, they may provide less accurate results for underrepresented groups.
- Ethical AI in healthcare means ensuring equal medical care for all patients.
- Fairness requires including diverse patient data and making diagnostic tools transparent.
- In 2025, regulators demand bias-free healthcare AI because unfair treatment can risk human lives.
AI in Education: Equal Opportunities for All
Education has seen a huge shift with AI-driven personalized learning platforms and automated assessments. But without fairness:
- Students from certain backgrounds may not get equal recommendations.
- Language models may favor learners from specific regions.
To ensure fairness:
- AI in education must provide equal access to resources.
- Transparency in grading systems and curriculum recommendations is critical.
- Schools and governments in 2025 are adopting ethical AI guidelines to protect student rights.
AI in Business and Finance: Transparency & Trust
In finance, AI is used for loan approvals, fraud detection, and investment decisions. But biased algorithms can:
- Reject loan applications from specific communities.
- Treat small businesses unfairly compared to larger corporations.
For fairness, financial AI must:
- Follow clear accountability frameworks.
- Use bias detection tools to ensure decisions are transparent.
- Provide customers with an explanation for approvals or rejections.
Businesses that apply responsible AI practices gain long-term trust and avoid legal risks.
AI in Government and Public Policy
Governments worldwide are adopting AI for public services, smart cities, and law enforcement. But here the stakes are high:
- Predictive policing AI can unfairly target certain communities.
- Welfare systems may unintentionally deny benefits to deserving citizens.
To ensure fairness in government use of AI:
- Strong governance and regulation must be applied.
- Public accountability and citizen oversight mechanisms are essential.
- Policies in 2025 emphasize responsible, transparent AI adoption in public sectors.
Global Regulations and AI Fairness Laws?
As AI becomes central to daily life, governments and organizations around the world are creating laws, policies, and regulations to ensure that AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable. By 2025, global regulation of AI has shifted from theory to practice, making AI fairness laws one of the hottest topics in technology policy.

EU AI Act and Ethical Guidelines
The European Union (EU) is leading the way with the EU AI Act, the first comprehensive law regulating artificial intelligence.
- The Act categorizes AI into risk levels (minimal risk, limited risk, high risk, and prohibited).
- High-risk AI systems (like those in healthcare, education, and policing) must follow strict fairness, transparency, and accountability standards.
- The EU has also set ethical guidelines for trustworthy AI, which include human oversight, non-discrimination, and explainability.
This makes Europe a global pioneer in shaping fair and responsible AI governance.
US AI Fairness Standards
In the United States, AI regulations are still industry-specific but are growing stronger:
- Agencies like the FTC (Federal Trade Commission) emphasize fairness in AI used for credit scoring, advertising, and hiring.
- The White House Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights highlights principles such as privacy, transparency, and equal treatment.
- Tech companies in the US are also voluntarily forming AI ethics boards to ensure compliance.
In 2025, US policies focus on balancing innovation with fairness and accountability.
Asia and Middle East Approaches to Responsible AI
- China has strict AI governance rules focusing on data security, censorship, and algorithm transparency.
- Japan and South Korea emphasize AI ethics in robotics, healthcare, and automation.
- Middle Eastern countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are adopting AI fairness frameworks to align with their smart city and digital economy initiatives.
These regions highlight how AI regulation is shaped by cultural, political, and economic priorities.
The Need for Global Collaboration in 2025
While different regions have different approaches, one challenge remains: AI is global, but laws are local.
- Without international collaboration, companies may “AI shop” for countries with weaker rules.
- A global standard for AI fairness and ethics would ensure consistency and trust across borders.
- Organizations like the OECD and UNESCO are already working to create international guidelines for responsible AI use.
In 2025, the push for global cooperation is stronger than ever because fairness in AI is not just a national issue—it’s a human issue.
The Future of AI Ethics and Fairness
As we move deeper into 2025 and beyond, AI ethics and fairness are no longer optional—they are becoming a core requirement for building trust between humans and intelligent systems. The future of AI will depend on how well we address bias, accountability, and transparency while keeping innovation alive.

Emerging Trends in AI Fairness
Bias-free algorithms: New AI models are being designed with built-in fairness checks to reduce discrimination in hiring, lending, and healthcare.
Explainable AI (XAI): Systems that can clearly explain their decisions will dominate, as users and regulators demand transparency.
Human-AI collaboration: Instead of replacing humans, AI will increasingly be designed to support human decision-making, reducing unfair outcomes.
Role of Responsible AI in Shaping Society
- Healthcare: Fair AI ensures equal access to medical treatments and diagnoses across populations.
- Education: Ethical AI tools prevent unfair grading and bias against students from different backgrounds.
- Employment: AI recruitment platforms will adopt stricter fairness protocols to eliminate gender or racial bias.
Responsible AI will shape a future where technology serves humanity without discrimination.
Challenges Ahead
Even with strong laws and guidelines, challenges remain:
- Cultural differences in defining fairness globally.
- Complex AI models (like GPTs) that make transparency harder.
- Corporate resistance to stricter regulations due to cost.
The future of AI fairness requires balancing innovation with ethical responsibility.
Vision for 2030 and Beyond
By 2030, experts predict that:
- AI ethics boards will be standard in most global companies.
- International AI fairness treaties may exist, similar to climate agreements.
- AI will become more human-centric, focusing on inclusivity, equity, and trust.
The ultimate vision is a world where AI empowers all communities fairly, ensuring that technology benefits everyone, not just a few.
Conclusion
In 2025, the conversation around AI ethics and fairness has shifted from theory to urgent reality. As artificial intelligence continues to shape our healthcare, education, finance, and everyday decisions, ensuring that these systems are fair, transparent, and bias-free is no longer optional—it’s essential.

The rise of global regulations, the development of bias mitigation strategies, and the demand for responsible AI governance prove that fairness is the foundation of trust between humans and machines. Without fairness, AI risks amplifying discrimination; with it, AI can become one of the greatest tools for building a more inclusive and equitable world.
The future of AI is not just about smarter machines—it’s about ethical, human-centered intelligence that benefits everyone, everywhere. By embracing AI ethics and fairness today, we are building a safer, more transparent, and trustworthy digital future.
As businesses, developers, and policymakers, the responsibility lies with us to make sure AI serves humanity with fairness at its core.